Understanding 401(k)s and Roth IRAs
Choosing the right investment account for your retirement savings is a crucial decision. Two of the most popular retirement savings options are the 401(k) and the Roth IRA. Each has its unique benefits and potential drawbacks, and your best choice will depend on your financial situation and retirement goals.
Features of a 401(k)
A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement savings plan. It allows you to contribute a portion of your pre-tax salary to an investment account, potentially reducing your taxable income for the year.
- Employer Match: Many employers offer matching contributions, effectively providing you with free money towards your retirement.
- Higher Contribution Limits: As of 2023, you can contribute up to $22,500 annually if you’re under 50 years old, and up to $30,000 if you’re 50 or older.
- Immediate Tax Benefit: Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, lowering your taxable income.
- Limited Investment Options: Typically, investment choices are limited to a selection of mutual funds.
Features of a Roth IRA
In contrast, a Roth IRA is an individual retirement account offering tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Tax-Free Withdrawals: Since you contribute post-tax dollars, qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
- No Required Minimum Distributions: You are not required to start taking money out at age 72, offering more flexibility in retirement.
- Wide Range of Investments: You can invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and more.
- Contribution Limits: As of 2023, the contribution limit is $6,500 per year if you’re under 50 and $7,500 if you’re 50 or older.
Choosing Between a 401(k) and Roth IRA
Deciding between a 401(k) and a Roth IRA depends on several factors, including your current tax rate, expected tax rate in retirement, and financial flexibility needs.
For those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement, a Roth IRA might be more beneficial due to its tax-free withdrawals. Conversely, if you anticipate being in a lower tax bracket, a 401(k) could provide more immediate tax benefits.
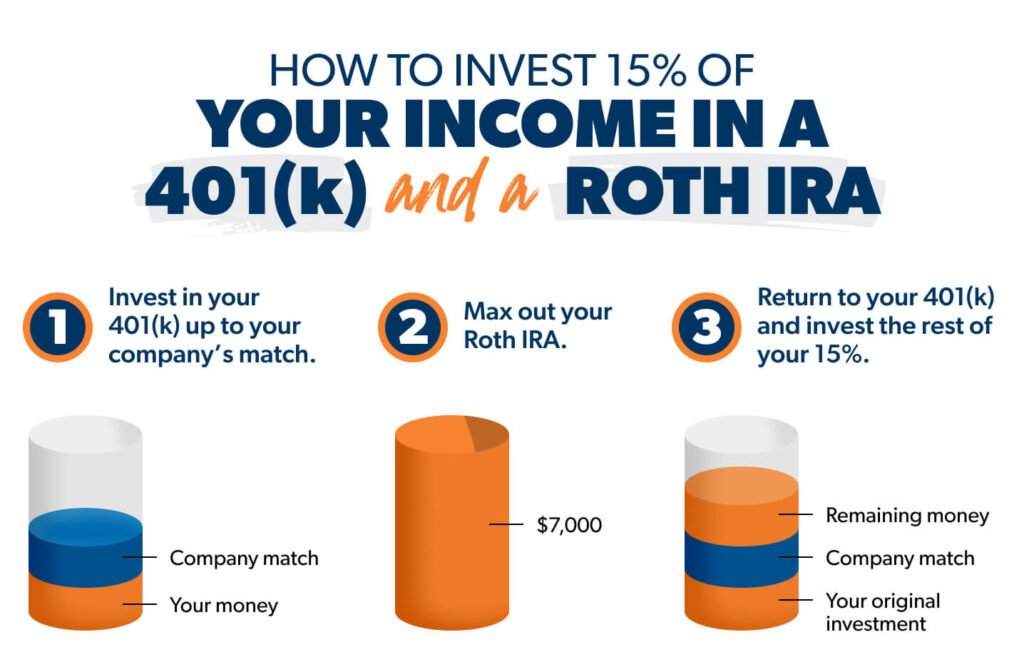
Ultimately, many financial advisors recommend a blended approach – maximizing your employer’s 401(k) match while also contributing to a Roth IRA, combining the benefits of both accounts. To effectively manage and optimize your retirement planning, consider using tools and resources that can guide you through the process.
Other Considerations
- Fees: Be aware of different account fees, as they can significantly impact your long-term savings.
- Withdrawal Rules: Remember that early withdrawals from either account may incur taxes and penalties.
- Income Limits: Roth IRA has income limits that may prevent high earners from contributing directly.
By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of both options, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your retirement goals and overall financial plan.